The central role of slitting machines in the production of PE, PP, PET films
The slitting machine plays a vital role in the production process of PE (polyethylene), PP (polypropylene) and PET (polyester) films, and its core role is not only reflected in the efficiency improvement of post-processing, but also directly affects the quality, cost control and market competitiveness of the finished film. The following are the specific roles and technical points of slitter in the production of these three types of films:
1. The core role of the slitting machine
(1) Specification customization
• Slitting width: The wide original film (such as the parent roll with a width of 6-8 meters) is slitted into the narrow width (such as 10mm-2000mm) required by customers to meet the needs of different industries such as downstream packaging, electronics, and construction.
• Roll diameter control: adjust the diameter of the coil (such as Φ200mm-Φ800mm) through the automatic winding system to adapt to the station requirements of terminal equipment (such as printing machines and laminating machines).
(2) Quality optimization
• Defect removal: Identify and remove crystal spots, bubbles, scratches and other defects on the surface of the film through the visual inspection system to improve the yield rate (for example, the yield rate of PET optical film can reach more than 99.5% after slitting).
• Edge treatment: high-precision slitting to avoid burrs (especially PP film is easy to fibrosis) to ensure the quality of lamination in the subsequent lamination or coating process.
(3) Efficiency improvement
• High-speed slitting: The slitting speed of PE/PP film can reach 800-1200m/min, and the hardness of PET film is usually 300-600m/min, which significantly shortens the delivery cycle.
• Automatic roll change: reduce manual intervention, and the switching time from parent to finished roll can be compressed to less than 30 seconds.

2. Technical points for different film materials
(1) PE film (soft, high elongation)
• Tension control: use low-tension slitting (such as 2-10N/cm²) to avoid tensile deformation; Equipped with a floating roller device to dynamically adjust the tension.
• Tool selection: Use a sharp round knife (hardness HRC60 or above) or ultrasonic slitting to prevent sticking.
• Static Elimination: PE is prone to static electricity, and it is necessary to integrate an ionic air bar to prevent the coil from absorbing dust.
(2) PP film (strong rigidity, easy to embrittle)
• Temperature management: the ambient temperature of slitting should be kept at 20-25°C (PP is easy to brittle at low temperatures).
• Slitting angle: The blade tilt angle is adjusted to 30°-45° to reduce edge stress cracking.
• Winding pressure: Gradually decreasing tension control, the outer layer pressure is lower than the inner layer (e.g. from 15N to 8N) to prevent the "hard core" phenomenon.
(3) PET film (high hardness and high precision required)
• High rigidity slitting: the use of diamond-coated tools can extend the service life by more than 3 times (especially suitable for electronic grade PET film with a thickness of <0.05mm).
• Dust removal system: equipped with clean room level air purification to avoid particulate adhesion (e.g. for LCD screen optical film).
• On-line detection: Infrared thickness gauge monitors thickness uniformity (tolerance ± 0.5μm) in real time.
3. Solutions for special process scenarios
• Multi-layer co-extruded film: the peeling between layers needs to be controlled during slitting (such as PE/PA composite film), and low-temperature slitting or pre-heating process (60-80°C) is used.
• Aluminized film slitting: Aluminium layer protection technology (e.g. soft contact guide rollers) prevents the metal layer from falling off.
• Ultra-thin film (<5μm): magnetic levitation slitting technology to avoid mechanical contact damage.

4. Impact on production costs
• Material utilization: By optimizing the knife arrangement scheme (such as nesting and slitting), the edge material loss of PE/PP film can be controlled within 1.5%.
• Energy consumption comparison: servo motor slitting is 20-30% energy-saving compared with traditional mechanical type, especially for the long-term production of PET film.
• Labor cost: 1 automatic slitting machine can replace 3-5 workers and reduce waste caused by human error.
5. Industry application cases
• PE plastic wrap: After slitting, it needs to pass the friction coefficient test (COF<0.3), and the slitting machine needs to ensure that there are no scratches on the surface.
• PP capacitive film: the slitting width tolerance ± 0.1mm, otherwise the dielectric properties will be affected.
• PET release film: Maintain the stability of the release force (e.g. 5-15g/in) after slitting.

Future Trends
• AI intelligent slitting: Predict tool wear cycles through machine learning and automatically adjust slitting parameters.
• Green manufacturing: online recycling and granulation of slitting waste (especially for PE/PP) to achieve closed-loop production.
summary
The slitting machine is the key conversion equipment for PE, PP, PET film from primary products to high value-added finished products, and its technical adaptability (such as tension control, dust removal, tool design) directly determines the terminal performance of the film. Enterprises need to choose a slitting solution according to the material characteristics (such as the ductility of PE and the rigidity of PET), and at the same time combine digital tools (such as MES system) to achieve full-process traceability to meet the strict requirements of high-end applications (such as new energy and flexible display).
Recent Post
 Efficient and precise! Analysis of the core functions of the paper tube cutter22. April, 2025
Efficient and precise! Analysis of the core functions of the paper tube cutter22. April, 2025 The era of intelligent slitting: how to simplify the operation of PLC control + man-machine interface?21. April, 2025
The era of intelligent slitting: how to simplify the operation of PLC control + man-machine interface?21. April, 2025 How does a slitting machine empower multi-industry production? Inventory of core application scenarios21. April, 2025
How does a slitting machine empower multi-industry production? Inventory of core application scenarios21. April, 2025 An overview of the slitter's functions: from basic operations to advanced cutting techniques19. April, 2025
An overview of the slitter's functions: from basic operations to advanced cutting techniques19. April, 2025
 Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus
Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts) Paper Core Loading Machine
Paper Core Loading Machine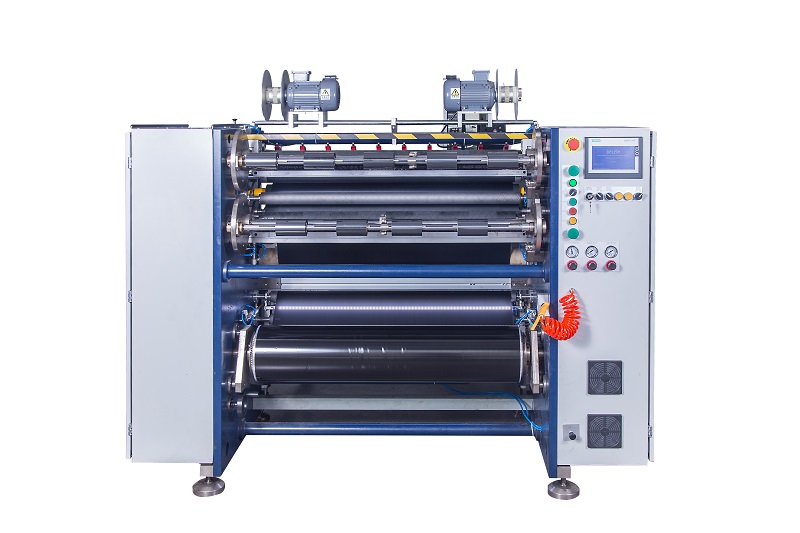 Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus
Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus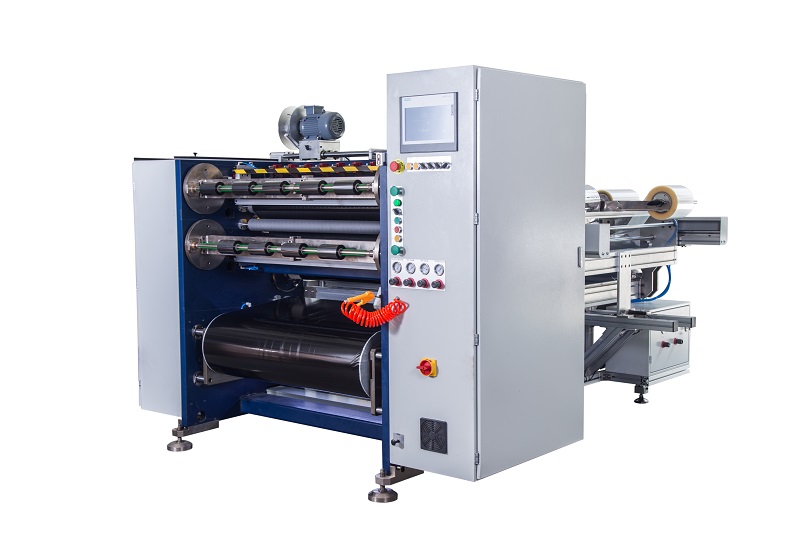 Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus
Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus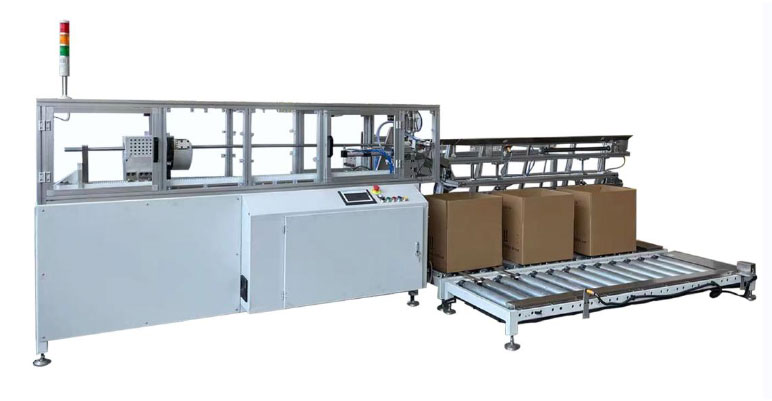 Auto Paper Core Cutter
Auto Paper Core Cutter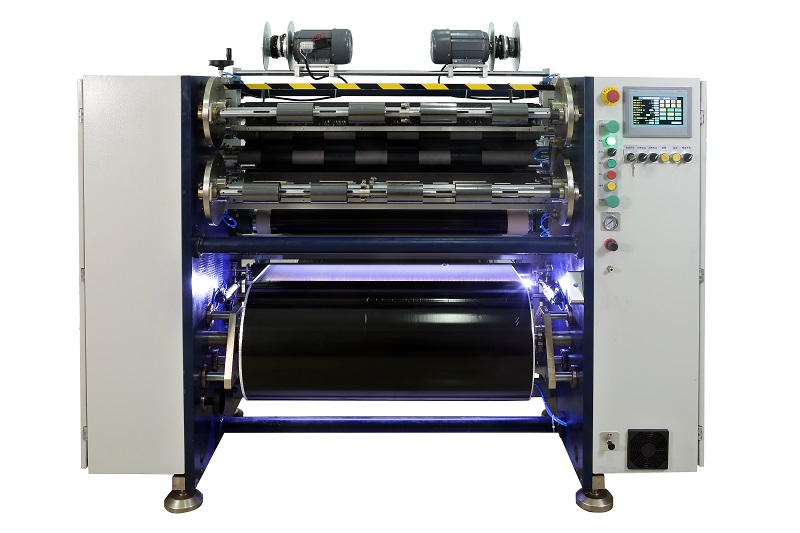 Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2
Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2