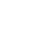Analysis of the application field of slitting machine: which industries cannot do without it?
Due to its efficient and precise cutting ability, slitting machines have become key equipment in the production chain of many industries. The following is an analysis of the indispensable core application areas of the slitter and their specific needs:
1. Packaging and printing industry - high speed and clean cutting
1. Flexible packaging materials
◦ Applications: Food packaging film (PE/CPP), aluminum-plastic composite film (e.g. snack bags), label substrate (BOPP).
◦ Requirements: no dust and burrs should be used during slitting to avoid polluting the contents; High-speed slitting (more than 600m/min) matches the efficiency of the packaging line.
◦ Example: Tetra Pak slitting needs to ensure smooth edges to prevent material delamination during the filling process.
2. Paper and cardboard
◦ Application: toilet paper slitting, cardboard (gift box), corrugated cardboard slitting.
◦ Requirements: anti-static treatment (to avoid paper sticking); Precise tension control to prevent tissue paper breakage.

2. New energy industry - micron-level accuracy and safety requirements
1. Lithium battery manufacturing
◦ Application: positive and negative electrode pieces (copper foil/aluminum foil), separator (PE/PP) slitting.
◦ Key requirements:
▪ No burrs: Metal dust can cause a short circuit in the battery, requiring a laser or ultra-precision knife.
▪ Tensile stability: The tensile deformation of the diaphragm affects the ion conduction efficiency.
◦ Data: The error of the slitting width of the pole piece needs to be ≤±0.05mm (such as the standard of CATL production line).
2. Photovoltaic industry
◦ Application: backsheet (PET), EVA film, solar cell silicon wafer slitting.
◦ Requirements: Clean cutting (no debris) to avoid hot spot effect after component encapsulation.
3. Electronic materials - ultra-thin and high-value material processing
1. Flexible Circuit Board (FPC)
◦ Application: mobile phone folding screen arrangement, sensor substrate slitting.
◦ Challenge: The thickness of the material is only 0.01~0.1mm, and laser slitting is required to avoid mechanical stress damage to the circuit.
2. Optical films
◦ Application: polarizer (OLED screen), brightness enhancement film (liquid crystal display).
◦ Requirements: dust-free workshop environment; The cutting edges need to be mirrored to prevent light scattering.
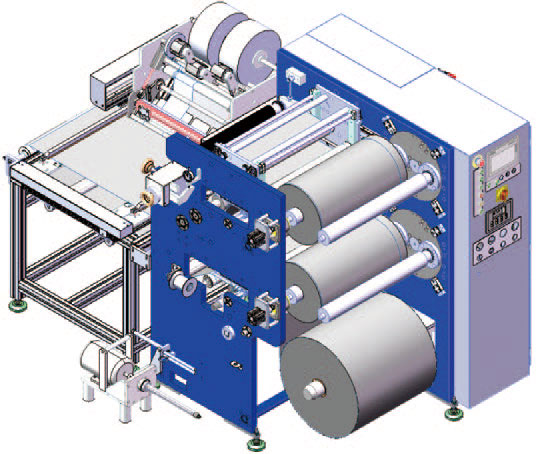
4. Textiles and composite materials - adaptability of diversified materials
1. Technical textiles
◦ Applications: carbon fiber prepreg (aerospace), glass fiber cloth (PCB substrate).
◦ Difficulty: The filament is easy to spread out, and the edge needs to be cured by ultrasonic or hot knife slitting.
2. Medical non-woven fabrics
◦ Application: Mask meltblown cloth, surgical gown raw material slitting.
◦ Requirements: Maintain material breathability; During the epidemic, the surge in production capacity has promoted the high speed of slitters (such as 300m/min).
5. Metal processing - high-strength and precision machining
1. Metal foils
◦ Application: copper foil (lithium battery), aluminum foil (capacitive electrode).
◦ Technology: round knife slitting + online deburring device, thickness can handle 5μm~0.2mm.
2. Composites
◦ Application: aluminum-plastic film (pouch battery), electromagnetic shielding film.
◦ Key point: When cutting in layers, it is necessary to avoid the separation of the metal layer and the plastic layer.
6. Emerging fields - technology iteration drives demand
1. Hydrogen fuel cells
◦ Application: Proton exchange membrane (PEM) slitting, which requires non-polluting, low-humidity environment operation.
2. Biodegradable materials
◦ Application: PLA/PBAT film (environmentally friendly packaging), low temperature control is required during slitting to prevent the material from sticking to the knife.
Summary table of industry dependencies
| industry | Core materials | Slitting accuracy requirements | Irreplaceable reasons |
| lithium battery | Copper foil/diaphragm | ±0.05mm | Safety risk (short circuit due to glitch) |
| Electron optics | Polarizers/FPCs | ±0.02mm | High-value material with extremely high cutting failure costs |
| Medical non-woven fabrics | Meltblown cloth | ±0.1mm | Sudden demand such as the epidemic relies on high-speed slitting |
| photovoltaic | EVA adhesive film | ±0.1mm | Affects the power generation efficiency of the module |
Future Trends
• Green slitting: Laser cutting replaces mechanical knives to reduce material loss (e.g., lithium battery separator slitting loss from 3% to 0.5%).
• Intelligent upgrade: Predict tool wear through AI (such as automatic tool change every 500km on Tesla factory slitter).
The slitting machine has become the "invisible champion" of the modern manufacturing industry, especially in the high-end fields such as new energy and electronics, and its precision and efficiency directly determine the performance of the end product. Enterprises need to choose slitting solutions according to the characteristics of the industry, for example, the lithium battery industry prioritizes explosion-proof design, while food packaging focuses on hygienic standards.
Recent Post
 An overview of the slitter's functions: from basic operations to advanced cutting techniques19. April, 2025
An overview of the slitter's functions: from basic operations to advanced cutting techniques19. April, 2025 Industry adaptability of slitter machine: a wide range of uses from packaging to new energy19. April, 2025
Industry adaptability of slitter machine: a wide range of uses from packaging to new energy19. April, 2025 Analysis of the core functions of the slitting machine: automatic deviation correction, tension control and waste edge recovery19. April, 2025
Analysis of the core functions of the slitting machine: automatic deviation correction, tension control and waste edge recovery19. April, 2025 High-precision cutting: How does the slitting machine achieve the ultimate slitting accuracy of ±0.1mm?18. April, 2025
High-precision cutting: How does the slitting machine achieve the ultimate slitting accuracy of ±0.1mm?18. April, 2025
 Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus
Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts) Paper Core Loading Machine
Paper Core Loading Machine Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus
Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus Auto Paper Core Cutter
Auto Paper Core Cutter Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus
Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2
Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2